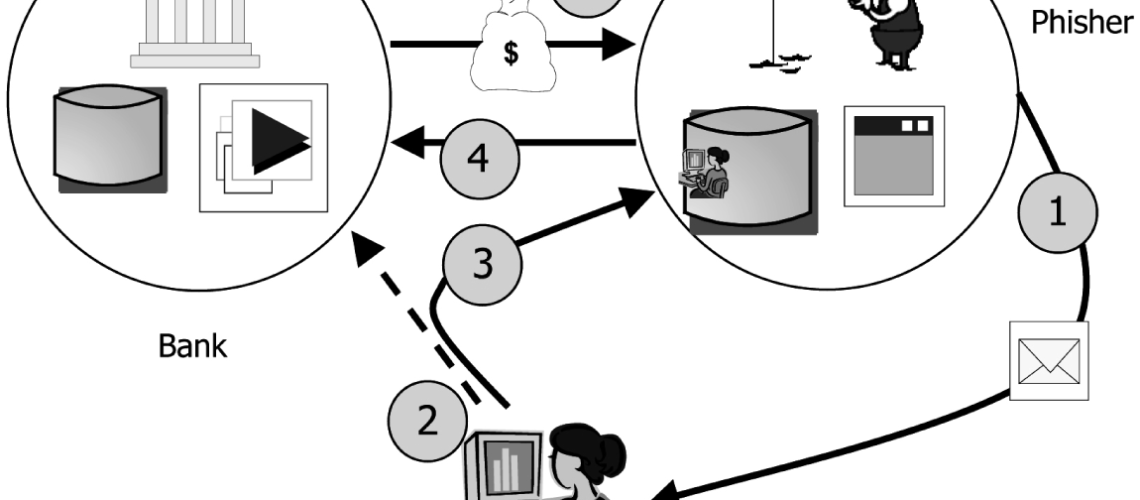
Phishing is a malicious attempt for acquiring sensitive information including passwords, usernames, security codes, details of credit cards, which is masked as a trustworthy electronic communication. This communication is pretending to come from popular social web sites, banks, auction sites, IT administrators and online payment processors, but it is actually coming from cyber criminals.
Phishing is a malicious attempt for acquiring sensitive information including passwords, usernames, security codes, details of credit cards, which is masked as a trustworthy electronic communication. This communication is pretending to come from popular social web sites, banks, auction sites, IT administrators and online payment processors, but it is actually coming from cyber criminals.
The phishing emails usually contain links to various websites that are infected with malware. The emails themselves are spread as instant messages or as email spoofing, deceiving users and directing them to enter personal details in fake websites that look just like the legitimate ones.
Phishing is a threat that is growing larger. The damage that can be done by phishing could range from a denial to access the email to a significant financial loss. The increased number of phishing incidents provoked certain legislation, technical security and public awareness measures.
Phishing in the Past and Today
The first phishing attempts were made in early 1995 by the AOHell program, tempting to hack the AOL users. The name of the term came from the popular hacker of the 90’s Khan Smith. This term was adopted as the most common HTML tag is'<><‘, and could not be detected by the AOL staff. The symbol resembles fish and thus came “phishing”.
In 2003 was registered the first known phishing attack against a bank. Later phishing started targeting clients using online payment services. In recent years, the main targets of the phishing campaigns are the social networking sites, aiming for identity theft.
At the end of 2013 was registered one of the largest phishing attempts when the Cryptolocker ransomware infected more than 250 000 PCs with email attachment of a Zip file pretending to be a customer complaint. The files of the users were locked by the ransomware, and the users got a request for payment against a key to unlock their files.Another piece of ransomware using phishing tactics is Cryptowall. In this case the attachment of the spam email contains malicious PDF files and .zip folders.
The Phishing Techniques
- Spear phishing – these are phishing attempts that are directed at certain companies or individuals. The attackers aim to collect personal information. This is the most successful fishing attack.
- Clone phishing – an attack based on a legitimate and previously used email that contains a link or attachment. The content or the address is cloned from an identical contact. The malicious message is sent from the email address which is masked to appear as coming from the original sender.
- Whaling – phishing attacks directed to senior executives at high-profile targets. A type of whaling phishing attack is the Rogue Wi-Fi attack.
The Phishing Methods
- Link manipulation – technical deception that makes a link appear to be from a certain organization. The phishers often use subdomains and URL addresses that are misspelled.
- Filter evasion – these are images that are not easy to spot by the anti-phishing filters. As an answer to them, the anti-phishing filters became more sophisticated and are now able to discover the text that is hidden in the images.
- Website forgery – the victim is lured to enter a phishing website and is directed to sign in. With this phishing attacks, the cyber criminals collect user names and passwords. They are especially dangerous when the website that has been forged is of a bank or a payment system. Such flaw was used against PayPal in 2006.
- Phone phishing – these are messages that pretend to come from bank officers. The users are lured into dialing a phone number in connection with problems with their bank accounts. This is how their account numbers and PIN are stolen.
- Pop-ups – they are set on the bank’s legitimate webpage and request credentials, making the users believe that the bank is the one who requests these details.
- Tabnabbing – a new technique using the tabbed browsing, directing the users to affected websites.
- Evil Twins – very difficult to detect, the cybercriminal makes a fake wireless network which looks like the legitimate network used in various public places. This is how they steal credit card information and passwords.
Anti-phishing strategies
Since 2007 many anti-phishing strategies has been applied in order to protect the personal and the financial data of the PC users. Today we apply several techniques to fight the phishing attempts. The web, phone and email phishing attempts can now be reported to the authorities.
Among the first strategies used is to train people to recognize such attempts and do not respond to them. In addition to that many anti-phishing measures have been embedded in the browsers for protection.
Naturally, legal actions were taken too. The first lawsuit against a suspected phisher was filed in 2004, and followed by many more. In 2005 was passed the Anti-Phishing Act by the Congress of the United States. Companies have also joined efforts to oppose the phishing attacks.