Both individuals and businesses are continuously being targeted by cyber criminals and their cruel inventions. As many security reports of 2014 and the first half of 2015 indicate – attack numbers are quickly increasing worldwide, reaching new, unbelievable peaks. Many questions regarding privacy and security still remain unanswered, or in better cases – partially answered.
Depending on whether you are a business owner, an individual user, or an employee of the corporative world, the tactics deployed by cyber crooks can vary. Am I a victim of a targeted attack, or a massive one? Is the purpose of the attack clear, or is it yet to be discovered? What kind of information was stolen from me? Are the people in my contact list also endangered?
As we can see, the questions emerging from malicious intentions can multiply quickly, as well as the ways used by virtual lawbreakers on a pro-rata basis. In a nutshell, to increase the quality of security, one has to be informed about the many pathways malware can follow back to his computer. And the more one knows, the harder they will become victims of online threats.
In the aspect of 2015, we have identified ten types of attacks. We have compiled recently active malware pieces, and we have listed them according to their severity. Starting from the most malicious ones.
→NB! 続行する前に, it is important to note that the threats we are about to list are intertwined, to a point where it may get quite tricky to categorize any piece of malware as one particular type.
ランサムウェア
Ransomware first entered the online space in 1989 when the AIDS Trojan a.k.a. PC Cyborg designed by Joseph Popp was introduced. AIDS Trojan is the first file-encrypting threat to encrypt the user’s files on the hard drive and demand money to unlock them. Since then, ransomware has evolved so much that a single ransomware piece – Cryptowall, has cost the world economy $18 million in less than a year. To put it in other words, Cryptowall’s creators have made millions of dollars while extorting money from individuals and businesses.
Other notable ransomware threats that have successfully ‘robbed’ users during the past year are:
- CryptoLocker
- Troldesh
- Bit Cryptor
- Tox Ransomware
- Alpha Crypt
- Los Pollos Hermanos
- Locker
To stay protected against ransomware, users should:
- Enable automated patches for the operational system and the web browsers.
- Limit to downloading software from safe providers.
- Block pop-up windows.
- Do not open emails sent by unknown senders.
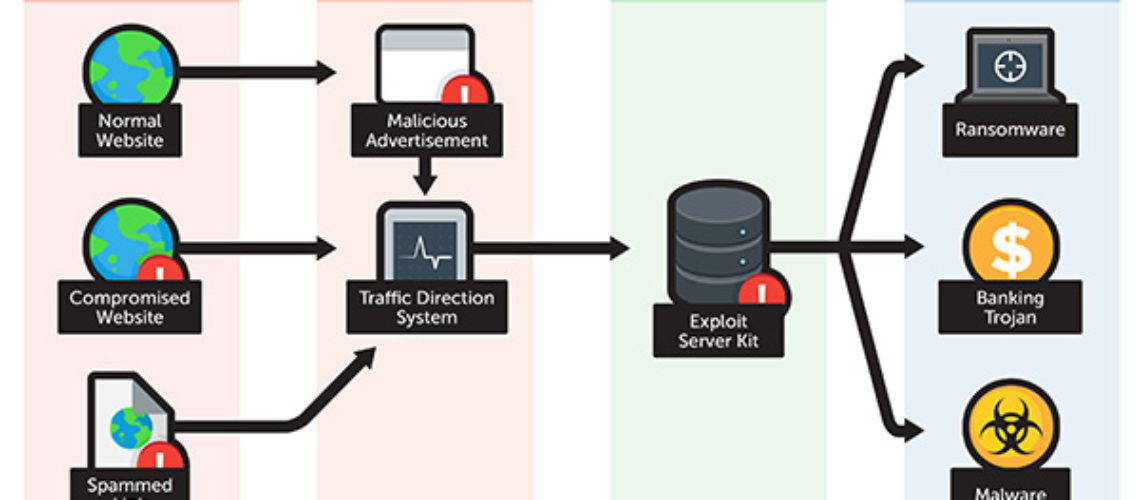
Exploit Kits
Since 2012, when the infamous Blackhole EK was detected in the wild, exploit kits have also generated a considerate amount of infections and are regarded a serious cyber threat. Even though different exploit kits may deploy different contamination tactics, the story usually goes as it follows:
- 1. The user visits a compromised website that has been attacked by cyber criminals.
- 2. The user experiences a series of redirects and ends up at a server hosting the EK.
- 3. The EK collects information about the victim’s system and determines how to proceed with the payload.
- 4. If the procedure is successful, the payload – malware, banking Trojan or Ransomware – is downloaded to the user’s PC.
Notable examples of exploit kits that have recently been detected are:
- Nuclear exploit kit
- RIG Exploit Kit (recently used to deliver CryptoWall)
- HanJuan exploit kit (also known as Timba Trojan and Fobber)
- Angler exploit kit
Since newer exploit kits are observed to exploit vulnerabilities preferably in Internet Explorer, Adobe Flash, and Adobe Reader, users need to update them regularly and enable automated patches where possible.
Banking Trojans
Two major financial stealers were eliminated back in 2014 – Gameover Zeus still active in 2017 and Shylock. しかしながら, instead of being shocked by their eradication, cybercriminals quickly moved forward and introduced Dyreza and Dridex to the financial world.
The Dridex Trojan, also known as Feodo, Bugat or Geodo, continuously attacked banking organizations. At one point, the malicious Trojan was exploiting the macros of the Microsoft Office Package. Even though macros are usually disabled by default by companies, cyber criminals are still trying to lure employers into enabling them.
Another vicious banking Trojan dubbed Vawtrak, Neverquest or Snifula, was also spotted. Once Vawtrak is activated, it gains access to the victim’s bank accounts and steals his login credentials. Vawtrak was distributed via:
- Drive-by downloads executed after opening a spam email attachment.
- Malware downloader.
- Exploit kit.
→As already visible, malicious attacks are becoming more sophisticated with time, implementing key features of the many-faced malware.
Collection of Malware, 寄生虫
Duqu 2.0 has been identified as the most sophisticated piece of malware ever seen. Correction – a collection of malware. Duqu 2.0 is a compound sequel of the Duqu worm that assimilates the features of a Trojan horse and a computer worm. Basically, Duqu is a sophisticated cyber espionage tool that even succeeded in compromising Kaspersky Lab’s security.
Kaspersky’s researchers have revealed that the targets of Duqu 2.0 are primarily linked to the negotiations about Iran’s nuclear deal. Several IT security companies were also targeted, as well as Western, Asian and Middle-East organizations. It is safe to assume that the design of Duqu 2.0 (and similar malware pieces) is not a joke to its creators.
PoS (Point-of-Sale) マルウェア
Malware targeting payment processing systems is not new to us. しかしながら, there is an increase in PoS malware variants. An older piece of PoS Malware first released in October 2013 – NewPoSThings – has once again been detected. Its recent attacks, in April 2015, indicated that the malware was directed at 64-bit machines with high version numbers.
Another PoS malware piece detected in 2015 is Punkey, set to deploy quite an aggressive point-of-sale operation to extract personal data. Regular victims of PoS malware are businesses – restaurants, casinos, resorts, hotels. Any place that requires or offers credit card payment can become a target.
Social Engineering Attacks
In security, social engineering is any psychological manipulation, resulting in making people perform certain actions or give away sensitive information. What differentiates social engineering from a regular con is the fact that it usually is a small junk of a more elaborate scheme. に 2015, we have already observed several attacks that employed some form of social engineering. Curiously enough, cybercrooks often turn to social media to utilize social engineering. E.g., a recent Facebook scam promised users 300 iPhones in exchange for clicking the Like button.
Social engineering attacks performed on the Web can be divided into four categories:
- Phishing – aimed at obtaining personal information.
- Pretexting – focused on making up a good pretext, a smart scenario, which will later be used in the attempt to gather compromised users’ personal information.
- Baiting – similar to phishing, with the difference that a prize item is offered to the victim.
- Quid pro quo – related to phishing and baiting. A service is offeredd instead of an item.
Fake Tech Support Services
It seems like fake tech support websites and lines never sleep. More and more fraudulent services are being reported on a daily basis. As a matter of fact, telling a real support line from a fake one is not a difficult task. しかしながら, crooks tend to exploit the negligence of average users. Plus, fake support scams usually come bundled with ad-supported software, aimed at widely used browsers.
Once the scam is activated, the user will start seeing pop-up windows claiming that his PC has been affected by multiple threats. Such pop-ups always provide a phone number that needs to be called. An example of such a number is 1-855-791-2391. To stay safe, users are highly recommended not to call the displayed number but to proceed towards scanning their systems. If such a call is initiated, remote access to the system may be obtained, and various credentials (including banking) may be harvested.
Rogue Antivirus Software
Rogue AV software is any software that is promoted as a useful anti-malware one. Instead of doing what it is advertised to do – shield the system against malware, the rogue AV program will do exactly the opposite. It will slow down the PC, compromise the user’s online safety, and make the system more vulnerable to malware attacks.
One example of a popular rogue is Antivirus Pro 2017. It is from the same family as Antivirus PRO 2015 and Defender Pro 2015.
一度インストール, the rogue antivirus tool start will begin performing a fake system scan. While scanning the system, multiple issues will be found. To regain control of his computer, running a real AV piece is a good idea.
不審なプログラム
Potentially unwanted applications and ad-supported software are not considered malicious, but they often open the gate to malicious online threats. PUPs are likely to have entered the system alongside another free app downloaded from the Web. The described method is legal, even though it may appear shady. It is called bundling and is primarily used to monetize various platforms and cover financial losses.
アドウェア
Our research indicates that hundreds of PUPs and ad-supported browser add-ons are released on a daily basis. To stay protected against the annoying third party intrusion, users should pay close attention to what they are downloading. Always read the EULA (End User License Agreement), Download Agreement, and Privacy Policy. Going for the advanced software installed that gives you the opportunity to view and deselect any added programs is also crucial.
*Article Sources:
HTTPS://blog.malwarebytes.org/intelligence/2013/02/tools-of-the-trade-exploit-kits/
http://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/financial-trojans-set-to-roar-back/
http://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/news/vulnerabilities-and-exploits/exploit-kits-past-present-and-future
http://cfoc.org/
http://sensorstechforum.com/
*Image Source:
http://www.trendmicro.com/